Class 11 CBSE Applied Maths Probability Exercise 12.4
Class 11 CBSE Applied Maths aims to develop an understanding of basic
mathematical and statistical tools and their
applications in the field of commerce (business/ finance/economics) and social
sciences. Topics covered in Class 11th Applied Maths includes : Numbers, Quantification and
Numerical Applications, Algebra, Calculus, Probability Distributions , Inferential Statistics, Index
Numbers and Time-based data , Financial Mathematics , Linear Programming.
Please Select
Q1. If P(AU B) = P(A) + P(B), then what can be said about the events A and B?
Solution :

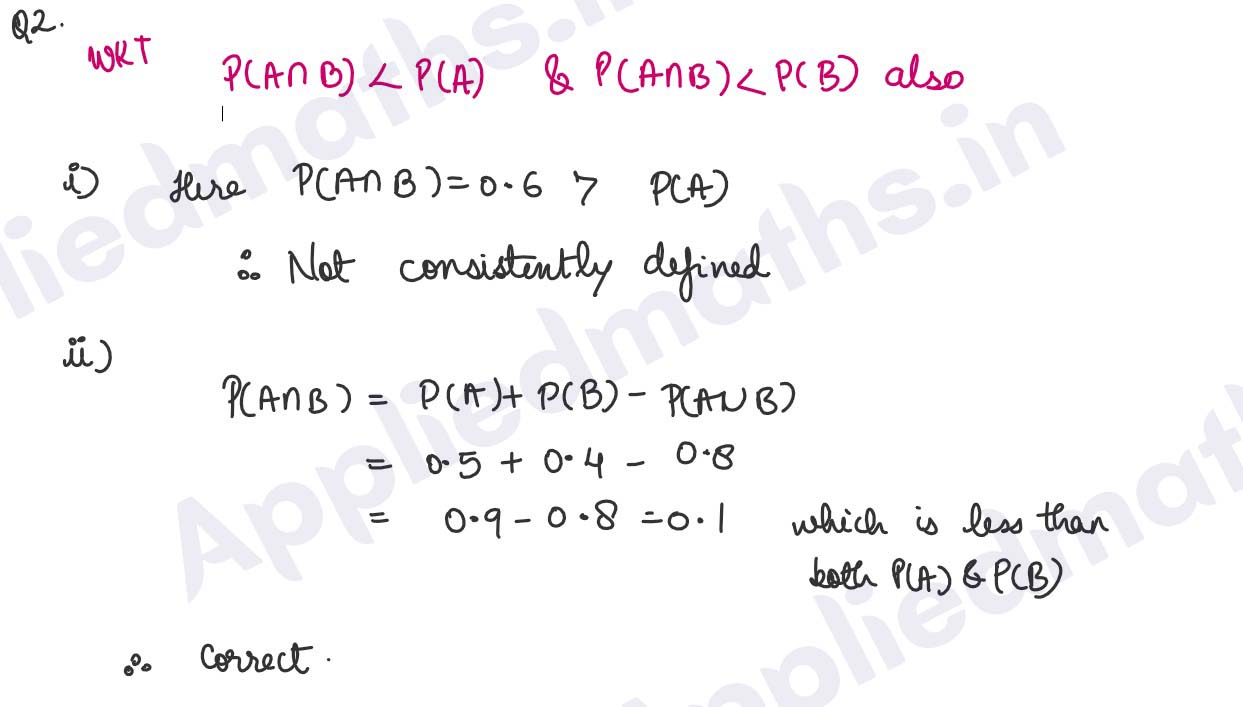
Q2.
Check whether the following probabilities P(A) and P(B) are consistently defined :
(i) P(A) =0.5, P(B)=0.7, P(A∩B) =0.6
(ii) P(A)=0.5, P(B)=0.4, P(AUB)=08
Solution :
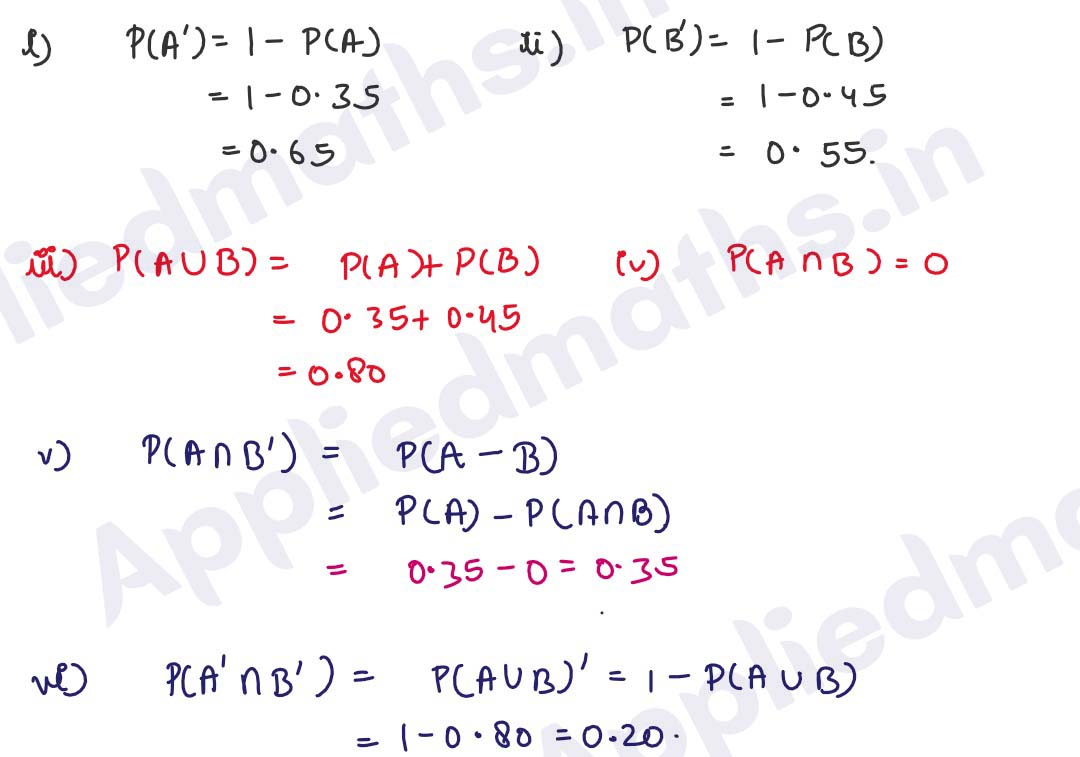
Q3.
If A and B are mutually exclusive events, P(A) = 0.35 and P(B) = 0.45, then find
(i) P(A') (it) P(B') (iii) P(AUB) (iv) P(A∩B)
(v) P(A∩B') (vi) P(A'∩B')
Solution :
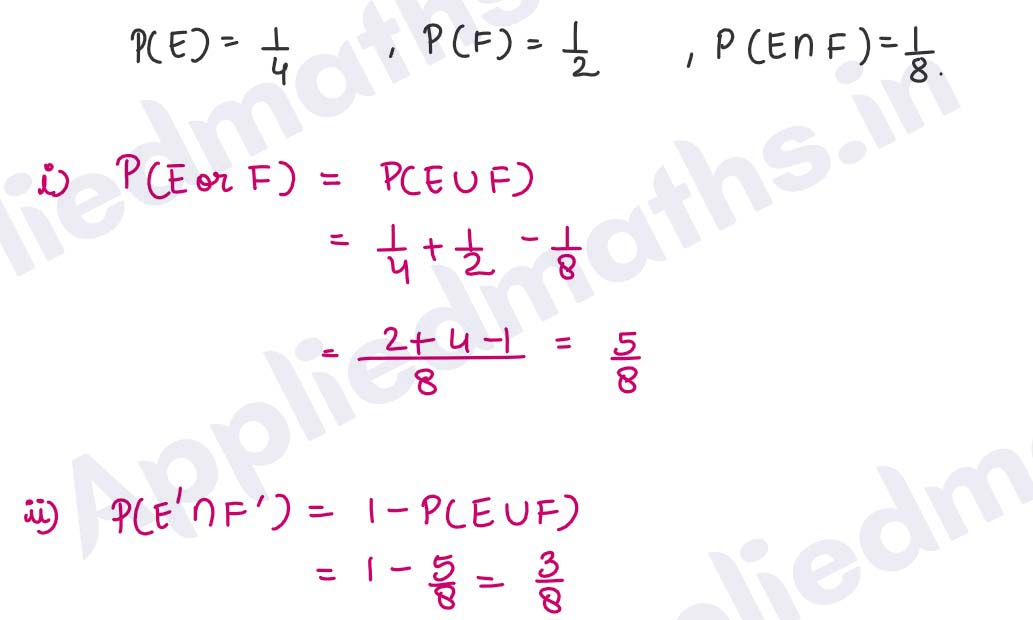
Q4.
If E and F are events such that P(E) = 1/4 and P(F) =1/2 and P(E and F) = 1/8 find
(i) P(E or F) (ii) P(not E and not F).
Solution :
Q5. If A, B and C are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events and it is known that P(A U B) = 0.63, calculate P(C).
Solution :
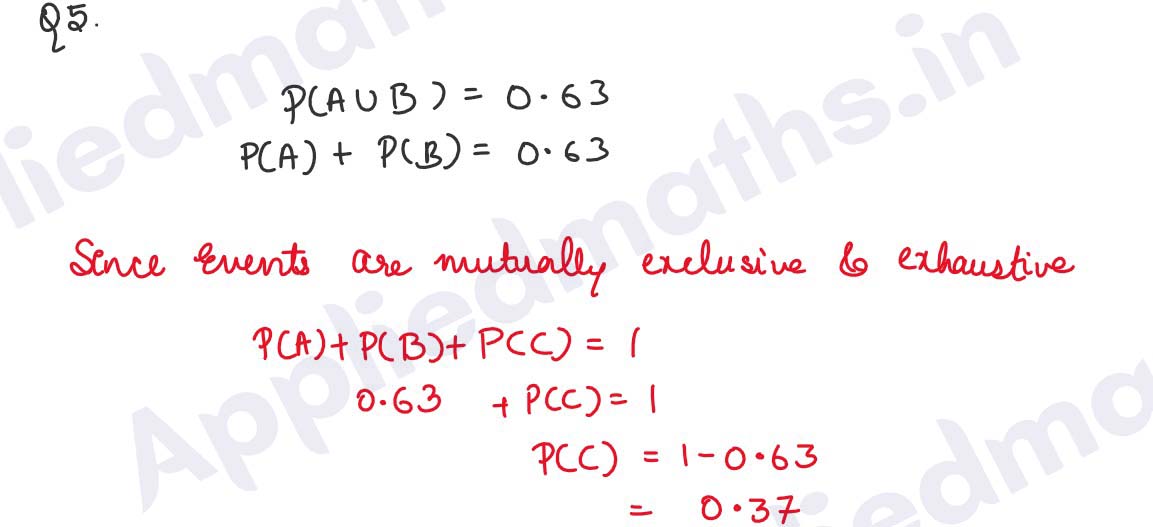
Q6. A, B, C are three mutually exclusive and exhaustive events associated with a random fe experiment. Find P(A), it being given that P(B) = 3/2 P(A) and P(C)=1/2 P(B)
Solution :

Q7.
The adjoining Venn diagram shows three events A, B and C,
and also the probabilities of the various regions (for instance
P(A∩B) = 0.07). Determine
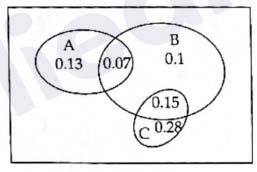
(i) P(A)
(ii) P(AUB)
(iii) P(B∩C) (iv) P(B∩C')
(v) P(A∩B')
(vi) Probability of exactly one of three events occurs.
Solution :

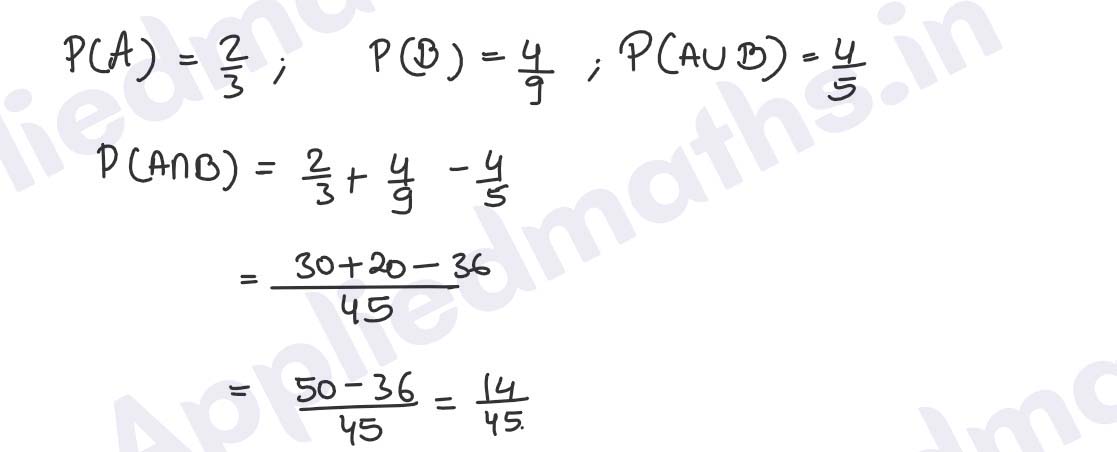
Q8. The probability that a contractor will get a plumbing contract is 2/3 and an electric contract is 4/9. If the probability of getting atleast one contract is 4/5, find the probability that he will get both contracts.
Solution :
Q9. Acard is drawn from a well shuffled pack of playing cards. What is the probability that it is either a spade or an ace or both?
Solution :
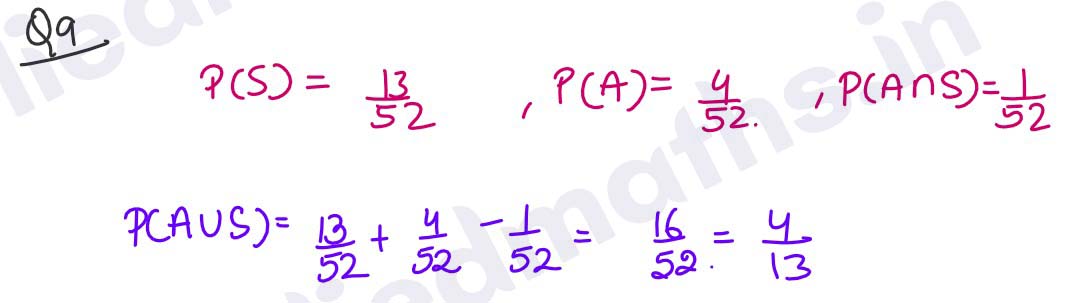
Q10. A card is drawn at random from a pack of 52 playing cards. What is the probability that the card drawn is neither a spade nor a queen?
Solution :

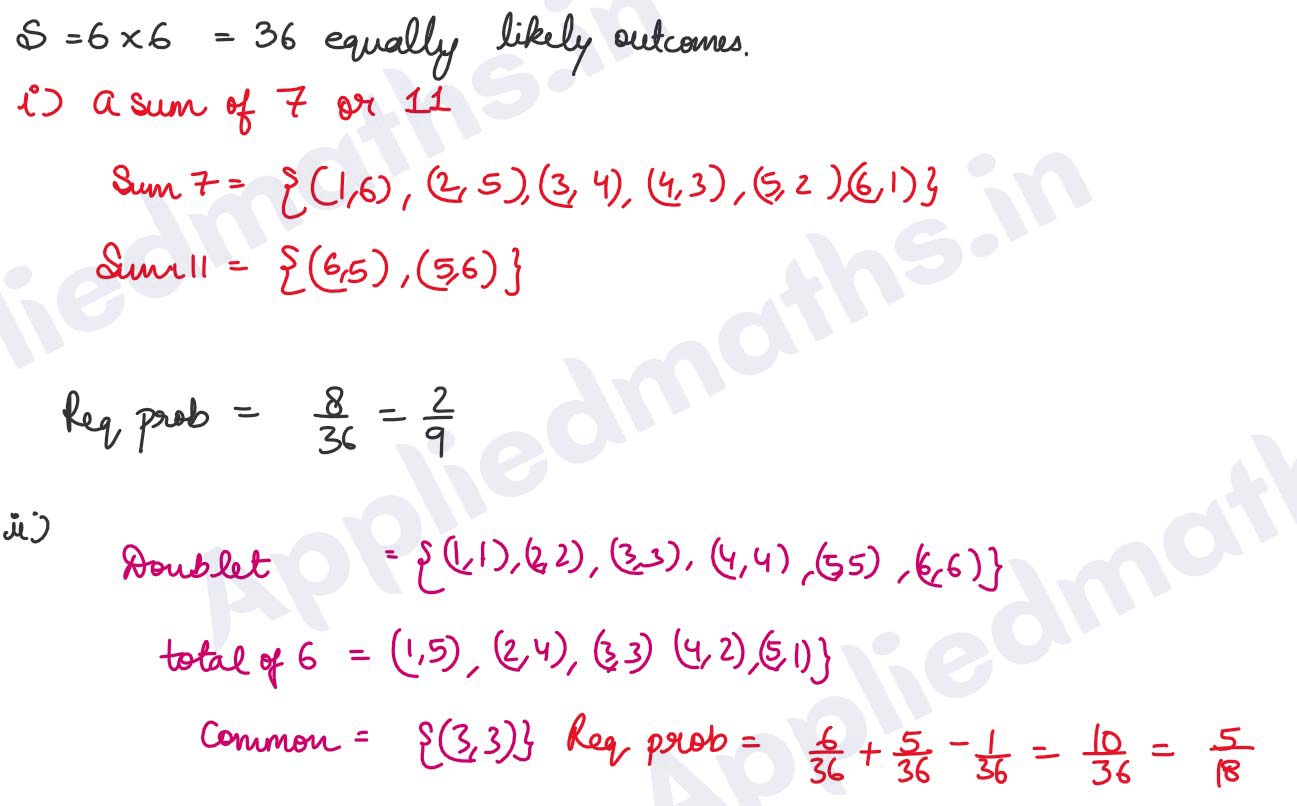
Q11. If two dice are thrown simultaneously, find the probability of getting (i) a sum of 7 or 11 (ii) a doublet or a total of 6.
Solution :
Q12. In class XI of a school, 40% students are punctual and 30% students are regular. 10% of the students are both punctual and regular. If a student is selected at random from the class, find the probability that he will be punctual or regular or both.
Solution :
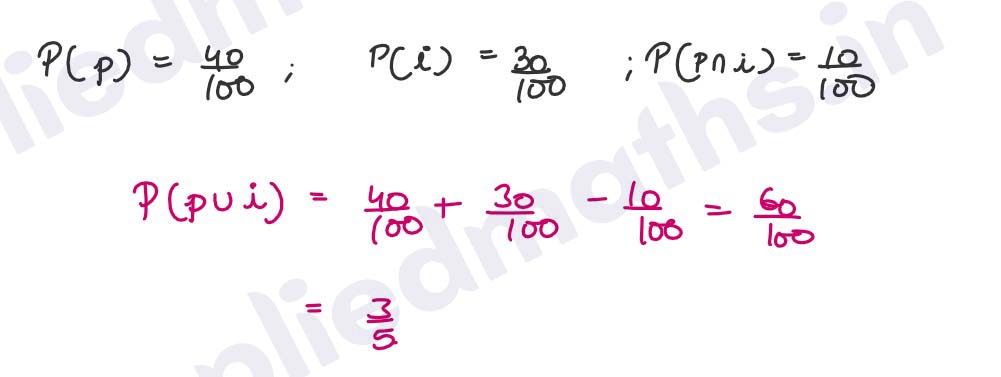
Q13. In an entrance test that is graded on the basis of two examinations, the probability of a randomly chosen student passing the first examination is 0.8 and the probability of passing the second examination is 0.7. The probability of passing atleast one of them is 0.95. What is the probability of passing both?
Solution :

Q14. The probability that a student will pass the final examination in both English and Hindi is 0.5 and the probability of passing neither is 0.1. If the probability of passing the English examination is 0.75, then what is the probability of passing the Hindi examination?
Solution :

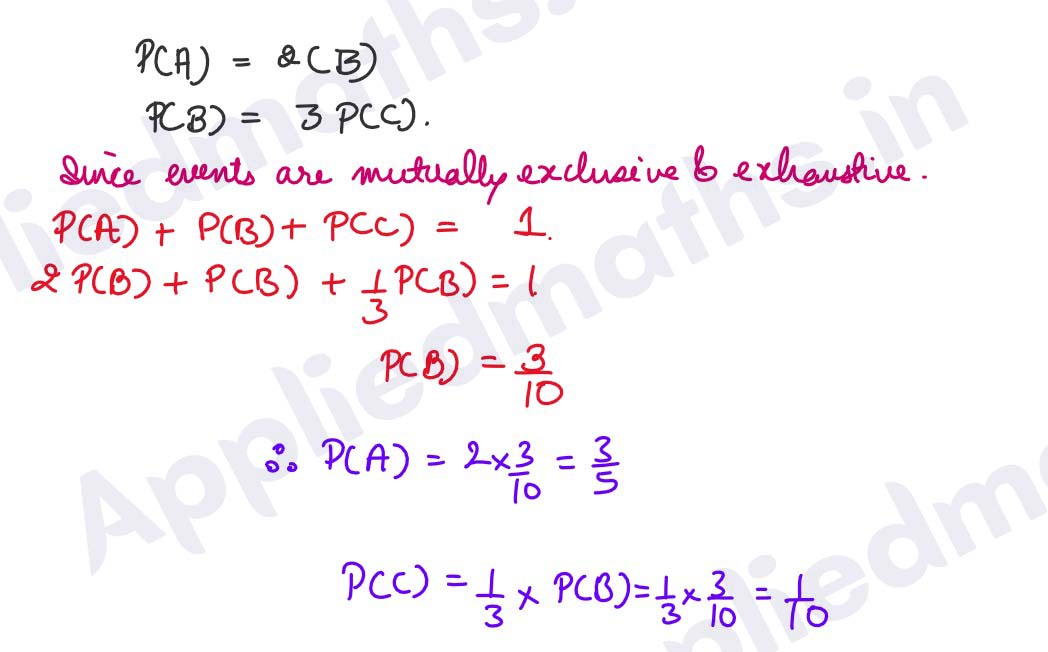
Q15. For a post three persons A, B and C appear in the interview. The probability of A being selected is twice that of B and the probability of B being selected is thrice that of C. If the post is filled, what are the probabilities of A, B and C being selected?
Solution :
Q16.
The probabilities that a student will get A, B,C or D grade are 0.4,0.35, 0.15 and 0.1 respectively.
Find the probability that she will get
(i) B or C grade
(ii) atmost C grade.
(ii) atmost C grade means C or D grade.
Solution :

Q17. Two cards are drawn at random from a pack of 52 cards. What is probability that the cards are either both aces or both black cards?
Solution :
